Bubble Sort - 冒泡排序
核心:冒泡,持续比较相邻元素,大的挪到后面,因此大的会逐步往后挪,故称之为冒泡。
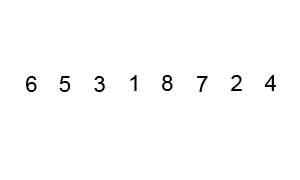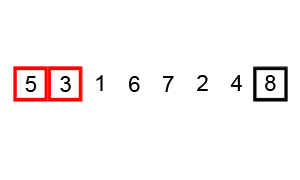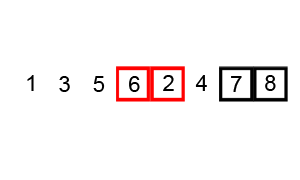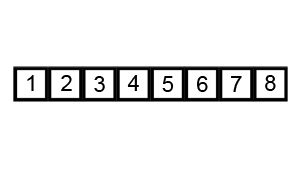
Implementation
Python
#!/usr/bin/env python
def bubbleSort(alist):
for i in xrange(len(alist)):
print(alist)
for j in xrange(1, len(alist) - i):
if alist[j - 1] > alist[j]:
alist[j - 1], alist[j] = alist[j], alist[j - 1]
return alist
unsorted_list = [6, 5, 3, 1, 8, 7, 2, 4]
print(bubbleSort(unsorted_list))
Java
public class Sort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int unsortedArray[] = new int[]{6, 5, 3, 1, 8, 7, 2, 4};
bubbleSort(unsortedArray);
System.out.println("After sort: ");
for (int item : unsortedArray) {
System.out.print(item + " ");
}
}
public static void bubbleSort(int[] array) {
int len = array.length;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
for (int item : array) {
System.out.print(item + " ");
}
System.out.println();
for (int j = 1; j < len - i; j++) {
if (array[j - 1] > array[j]) {
int temp = array[j - 1];
array[j - 1] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
复杂度分析
平均情况与最坏情况均为 , 使用了 temp 作为临时交换变量,空间复杂度为 .